
The content of the article:
- Main suspension functions
- Suspension elements design
- Spring suspension history
- Spring suspension design and operation
- Pros and cons of springs
The suspension plays an important role in the design of the car - it is on its operation that the smooth movement of the car on the roads depends. And since roads are not of very good quality, the load on the suspension increases several times. The leaf-sprung suspension has perfectly demonstrated itself just in the harsh operating conditions of cars. We will dwell on its design and principle of operation.
Main suspension functions
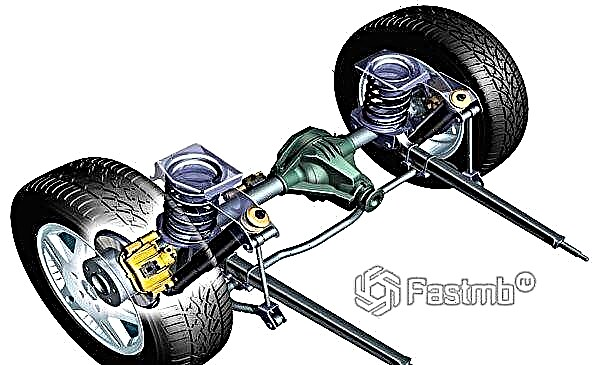
First of all, it should be noted that exactly suspension elements connect the car body to the tires... Without this element, the car turns into an ordinary cart, which shakes when the slightest irregularities appear.
Therefore, the first and main function of the suspension is to react to road irregularities, ensuring smooth movement of the car.
The second and also important function of the suspension elements is to increase the stability of the vehicle. During cornering and turning, the vehicle is subjected to external lateral forces that can result in a rollover. The suspension ensures the stability of the car, ensuring the safety of those in the cabin.
And finally, the third function, which was already mentioned earlier - the suspension connects the chassis to the body.
Suspension elements design
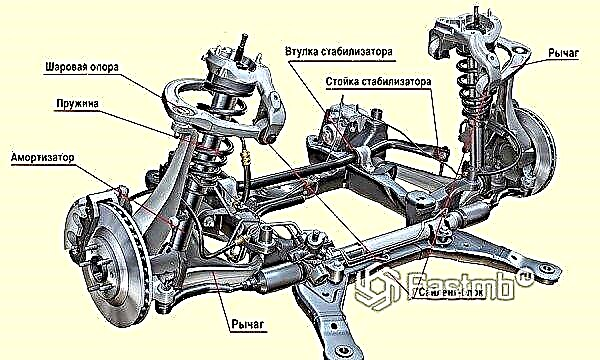
Any suspension consists of three components:
- quenching component;
- guiding component;
- elastic component.
The damping component, judging by the name, is needed to damp various irregularities that occur along the path of the car. Shock absorbers are most often used as this component.
The guiding component is represented by levers that serve to connect the chassis and body of the vehicle.
The elastic component is intended for the perception and transmission of forces arising from the tires hitting bumps. Due to the flexibility and elasticity, the reaction forces of the road are damped, so the driver does not feel unnecessary discomfort when driving on uneven surfaces.
It is generally accepted that there are two types of suspensions: mechanical and pneumatic. However, some suspension elements also combine electrical and hydraulic components to help achieve smoother road travel. Sometimes the electronic control unit is responsible for the operation of the suspension.
Spring suspension history

Suspension systems of this type appeared many years ago. In ancient Rome, springs were sometimes used on carts. Leather belts or metal chains were used as elastic elements. The use of such suspension systems made it possible to transport bulky goods without the potential danger of damaging the axles and wheels.
In our country, springs began to be used at the beginning of the 19th century on carriages, where springs were previously used. In the middle of the last century, springs were very popular on passenger cars, but later they began to be abandoned, equipping only heavy vehicles with springs.
Most trucks have spring suspension in their design, which makes it possible to transport bulky goods over long distances and on bad roads, without fear of unexpected damage to bridges and wheels.
Spring suspension design and operation
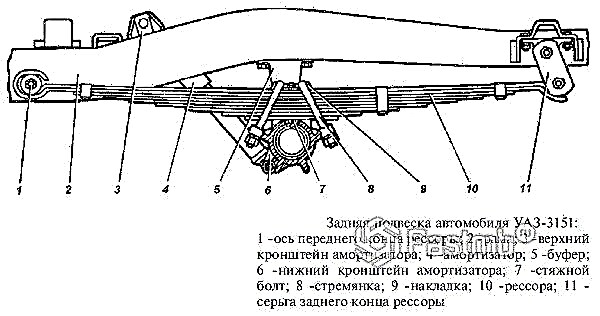
This suspension element is represented by metal springs - steel sheets of different lengths, which are fastened together with clamps. The center of the steel sheets is responsible for securing the suspension to the vehicle's axle. The ends of the sheets are attached to the machine frame using hinges or earrings.
It is not necessary to use several sheets, so in the middle of the last century in America, suspension systems with one metal sheet were used. Such systems were installed on Ford cars, and only a few years later this system gained its popularity among European automakers.
When hitting an obstacle, the spring leaves bend slightly, thus extinguishing all vibrations resulting from a collision. If there are several sheets, a large load falls on the lower spring, therefore it is made shorter, while achieving the smallest bending. The upper springs, on the contrary, are made longer in order to achieve greater flexibility and damp the remaining vibrations after the lower sheets.
Pros and cons of springs

The most obvious advantage of metal sheets is ease of manufacture, and therefore lower cost. Such structures are also distinguished by reliability, since it is extremely difficult to break down thick layers of metal.
Another significant plus is the increased stability of the car when performing some maneuvers. The spring takes on not only road loads, but also lateral loads that arise when making turns, as well as longitudinal ones that appear when the car accelerates and during braking.
Cars with spring systems are unpretentious to the quality of the roads - they can move freely along deserted highways. In addition, the load in the trunk will in no way affect the subsidence of the car, since all the loads from it will be extinguished by the spring.
The main disadvantage of the springs is the low service life of the metal sheets. Frequent loads lead to the subsidence of the metal, which results in grinding and rattling during the movement process. The spring will require constant lubrication, and the gaskets will often have to be changed.
Some motorists who use leaf springs complain about fixed costs, which are so high that the advisability of using leaf spring suspension becomes questionable. In some cases, it is easier to install a hydropneumatic suspension element, despite its high cost.
The use of spring systems in passenger cars is extremely rare. But if you operate a truck that is engaged in the constant transportation of goods, the leaf spring suspension will show itself in all its glory.